In order to ensure data security and accessibility, organizations often utilize technologies such as SharePoint or OneDrive for Business to store data in a centralized location. However, despite features that redirect folders to OneDrive, users still retain the ability to choose where to save data, including local or removable drives.
In this post, I will guide you through the process of preventing users from saving data on local or removable drives using Microsoft Intune. The steps involve leveraging the settings provided by Windows through the File Explorer CSP. You can find more information about the CSP in the File Explorer CSP documentation.
Note this process applies to Windows 11, version 21H2 and later.
To get started go to the Intune console, navigate to Devices -> Configuration Profiles. Then, create a new profile for the following specifications:
- Platform: Windows 10 and later
- Profile type: Settings Catalog
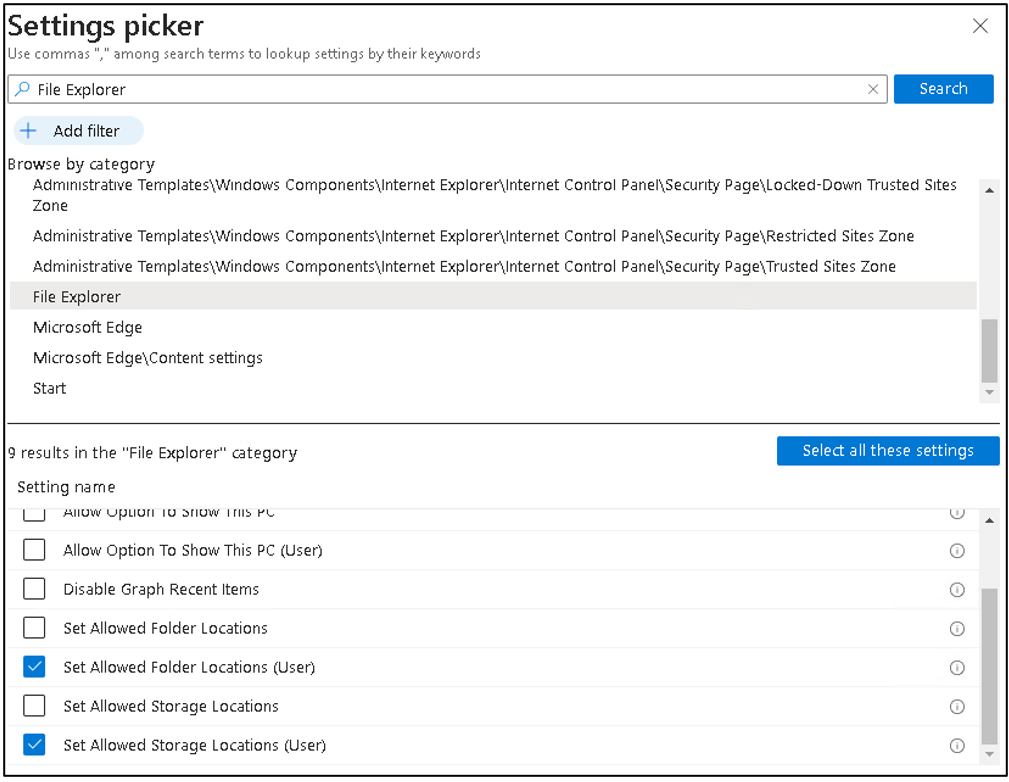
Next, provide a name for the policy and proceed to add the necessary settings: In the search bar, type “File Explorer” to locate the File Explorer category and add the following two settings to the policy:
- Set allowed Folder Locations: This setting allows you to specify specific locations that will be visible when the user opens File Explorer. These locations will be presented as options when the user attempts to save a file.
- Set Allowed Storage Locations: With this setting, you can define where users are allowed to store data. By adding “Syncroots,” you can include OneDrive for Business as an option. Depending on your requirements, you can adjust this setting to allow or restrict removable drives as well.
The policy settings look like this, first select the category and the settings.
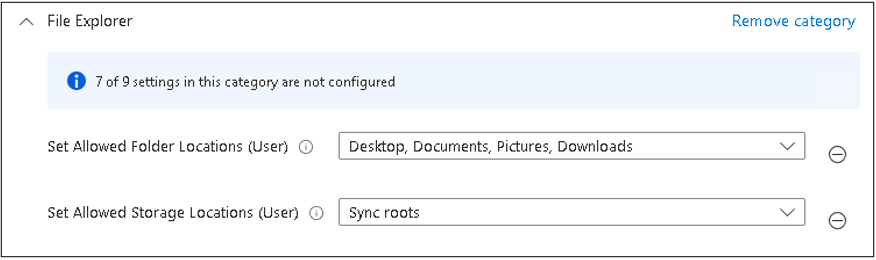
Then configure drives folders and storage locations the user can use.
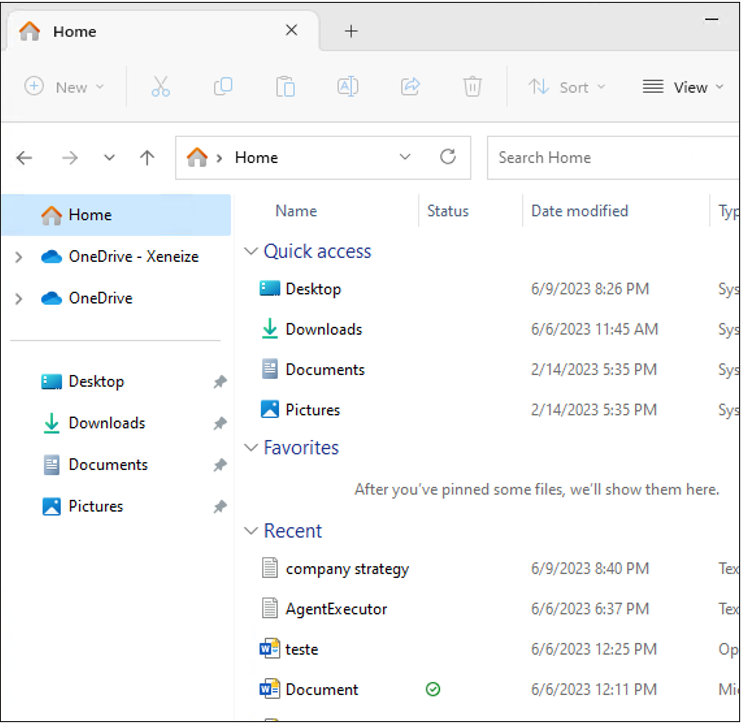
After configuring the policy, the next step involves assigning it to the appropriate user group and syncing the device. Once the policy is successfully deployed, the File Explorer interface will reflect the changes, and local storage options for data storage will no longer be available. Instead, the user will see the allowed storage locations specified in the policy.
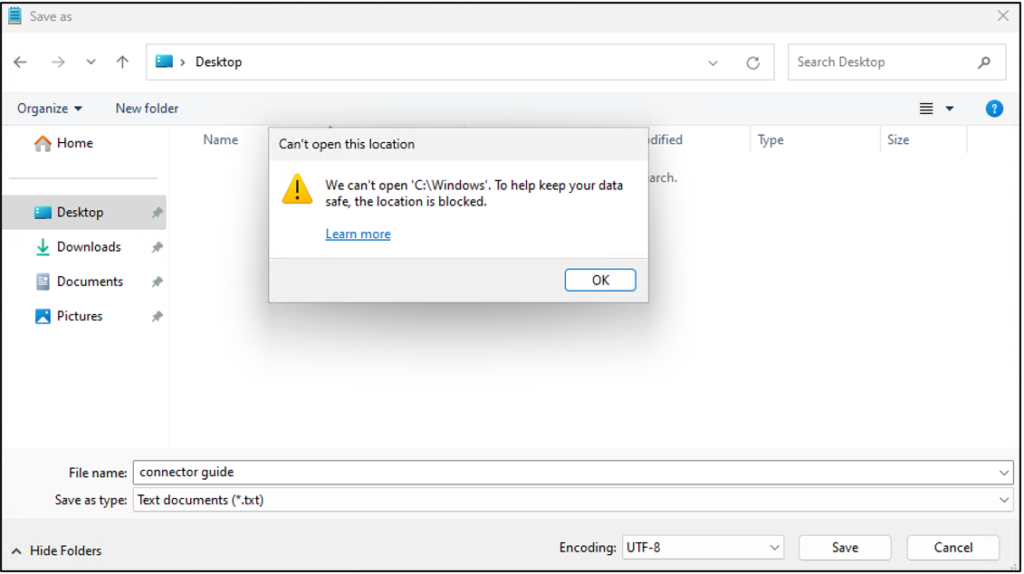
If the user enters the path to access C drive, a notification will be shown the same if they use other apps, like the command prompt.
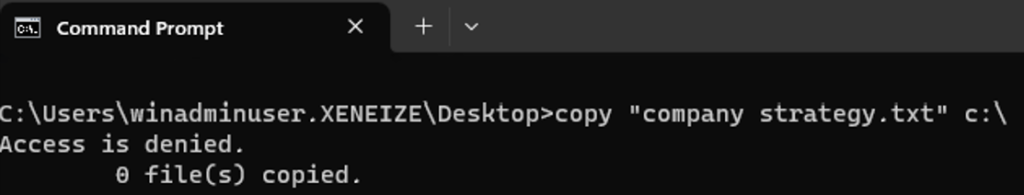
You may want to combine this policy with OneDrive for Business and redirect the known folders (Desktop, Documents) to One Drive. Hence no data will be stored on local drive.
Redirect and move Windows known folders to OneDrive: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/redirect-known-folders
By restricting the available storage options, you can enhance data security and encourage users to store their data in the designated locations provided by your organization.
